Visual Basic and Access were a great combination. They allowed the creation of small powerful apps, specially apps for data collection, or just applications that needed a small database that could run standalone.
A good option when you are upgrading your Access database and you do not need a centralized SQL Server (or that is just too much for your environment) is to migrate to other options like SQLite or SQL Server.
SQL Server has now a lot of versions (SQL Server Compact 3.5, SQL Server Compact 4.0, SQL Server Express and now even SQL Server LocalDB) a good table that compares this databases feature by feature can be located here: http://erikej.blogspot.com/2011/01/comparison-of-sql-server-compact-4-and.html)
If what you need is to support a simple, small (less that 4G) standalone database then using SQL Server Compact edition might be for you.
The main version for SQL Compact as at the moment 3.5 and 4.0.
Moving from Access to SQL Compact is not hard. There are many third party tools some free some not: http://erikej.blogspot.com/2009/04/sql-compact-3rd-party-tools.html
Primeworks tools are very easy to use, but you can also use the Microsoft SQL Server Assistant for Access (good links for this tools are in MSDN http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh313039.aspx and also the SSMA Blog http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ssma/)
SQL Server Compact uses the ADO.NET and OLE DB providers, and in many scenarios is just what you need. So take it as an option if you just need a replacement for MS Access
One of the first steps to put your database in Windows Azure is to put your data on the cloud.
1. The first step is to log in to Azure
1.a) Go to https://windows.azure.com/Cloud/Provisioning/Default.aspx
1.b)Type your user name and password.
1.c) When your are logged in go to SQL Azure option on the left hand menu.
1.d) You will see a list of your projects. Click on the project.
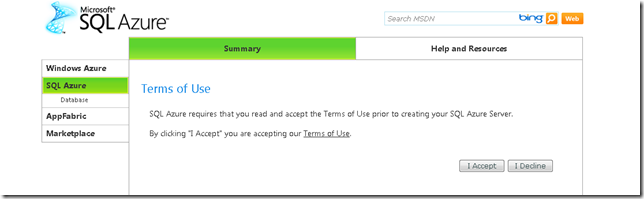
2. You must accept Azure Terms of Use
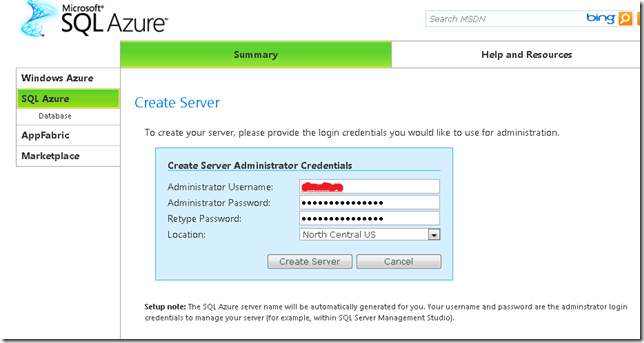
3. Now create a server. You must indicate an administrator username and password. Azure will set the server name.
Press the Create Server button and continue.
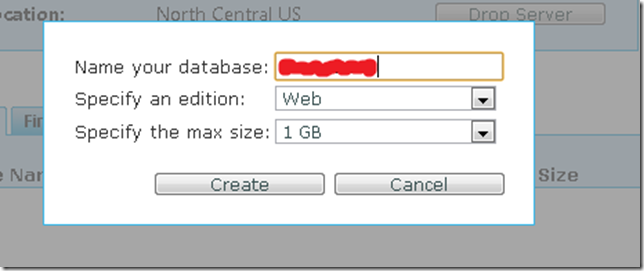
4. Now let’s create a new database.Press the Create Database Button
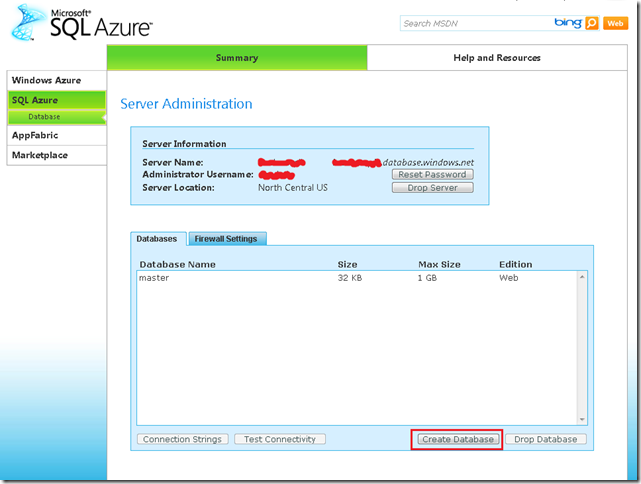
5. Just type your database name, edition and size. Editions can be Web or Business.
At this moment Size for Web Edition is 1GB or 5GB and for Business is 10GB, 20GB, 30GB, 40GB and 50GB.
Prices varies according to the options that you select.
For my purposes I will select a Web Edition of 1GB
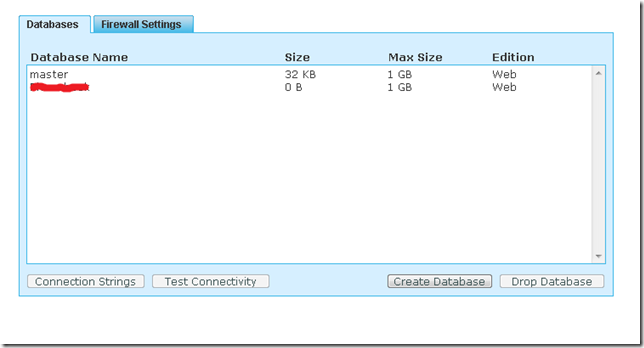
6. You should be able to see your new database in the Databases list.
7. Configure Firewall settings so you can connect to the new database.
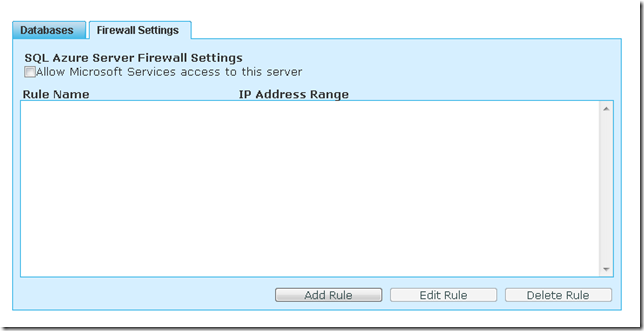
7.1 Press the Allow Microsoft Services access to this server checkbox.
That will add a Rule Name that allows access from 0.0.0.0 to 0.0.0.0.
Select the rule and press Edit. You must can type something like 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 to allow access to all IP Address.
Moving your data to SQL Azure
The easiest way to upload a SQL Server database to SQL Azure is to use
the SQL Azure Migration Wizard this is a great tool that you can download from
CodePlex http://sqlazuremw.codeplex.com/
1. Download the tool. In my case I installed it in D:\SQLAzureTools. Run SQLAzureMW.exe

2. Select SQL Database and press Next
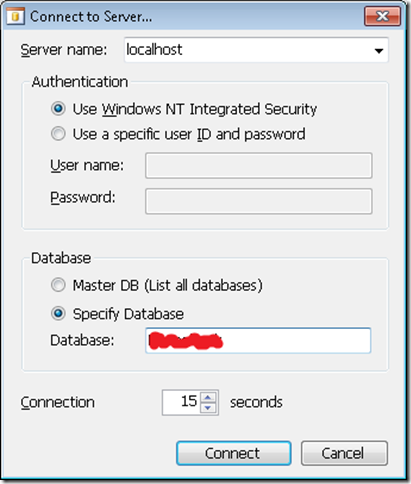
3. Select your database and press connect. That will add your database to a list. Click on your database name and press Next
4. Select the tables and other object that you will move to your SQL Azure database
5. Press Next a Summary is presented with all options
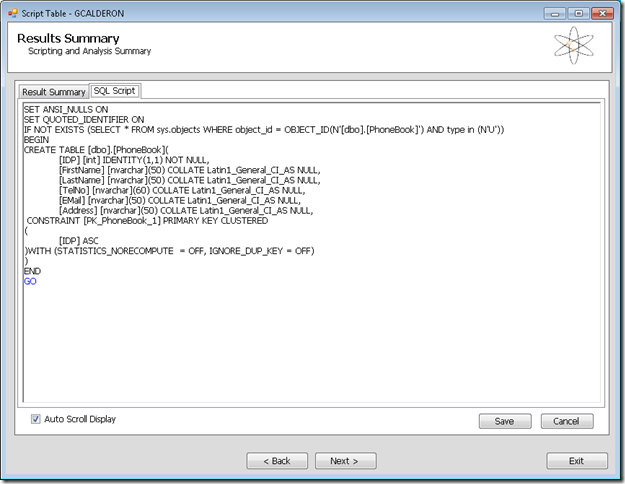
6. The wizard will generate a BCP file and a script for your tables.
You can connect to run your scripts with the following command:
> sqlcmd -S tcp:<servername>.database.windows.net -U <username>@<servername> -P <password> –d <database>
Depending on your configuration you might have problems with BCP. In general you need something like:
To export data:
bcp PhoneBook out c:\temp\Phonebook-c.dat –S <Server> –T –c
-T means a trusted connection and native format
To import data
bcp Phonebook.dbo.Phonebook in c:\temp\Phonebook-c.dat -c -U <username>@<servername> -P <Password> -S tcp:<servername>.database.windows.net -c
After importing your data, you are set to keep on developing your applications on Azure
NOTE:
If you dont know the schema name connect to your database and run something like:
SELECT '['+SCHEMA_NAME(schema_id)+'].['+name+']' AS SchemaTable FROM sys.tables